Lecture 6 - Thread¶
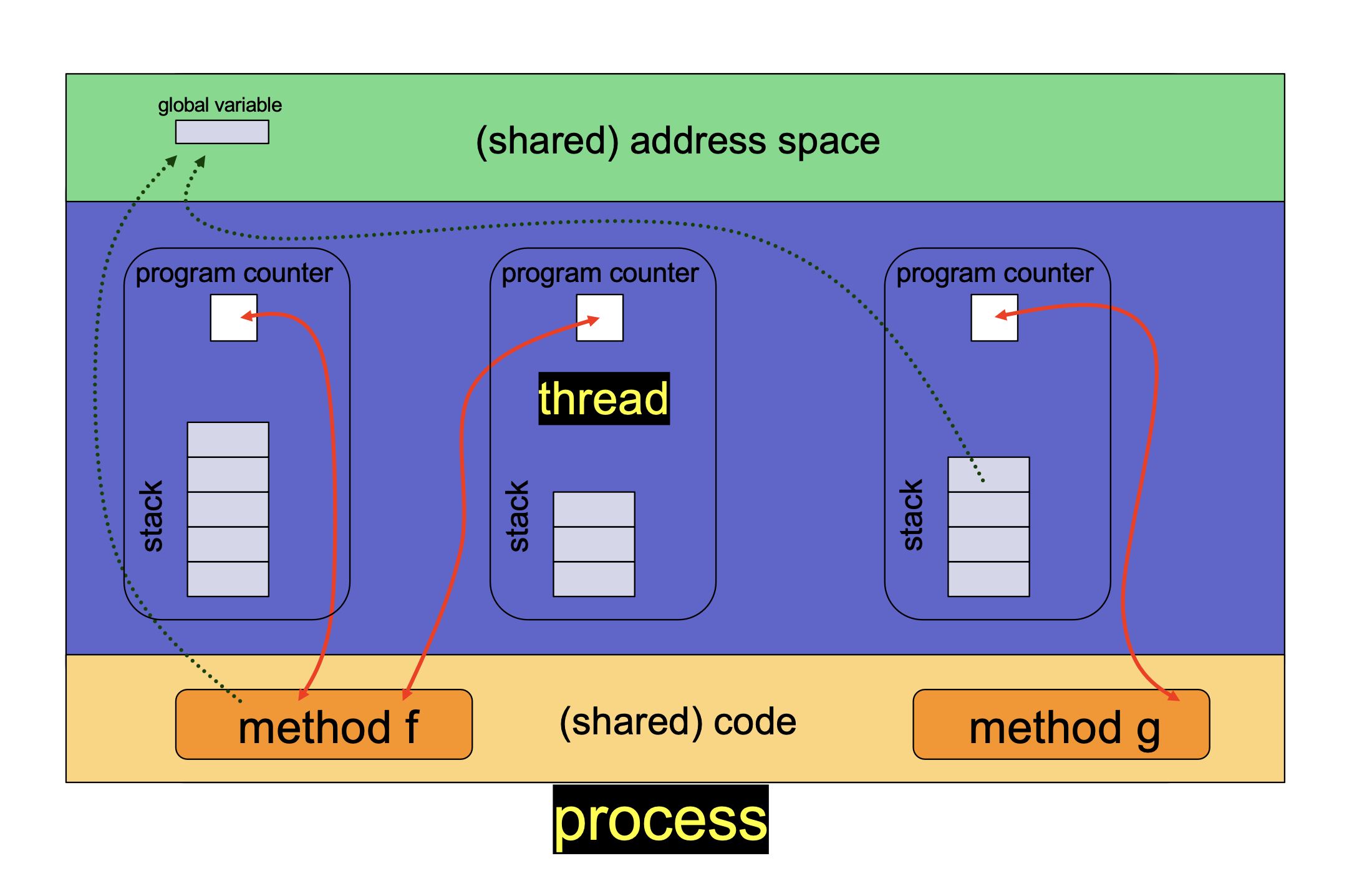
- A thread is a basic unit of execution within a process
线程是进程内的基本执行单元,进程是资源分配和隔离[allocation and protection]的基本单元
- A Process contains at least one thread, and can contain multiple threads
Revisit IMPORTANT!!
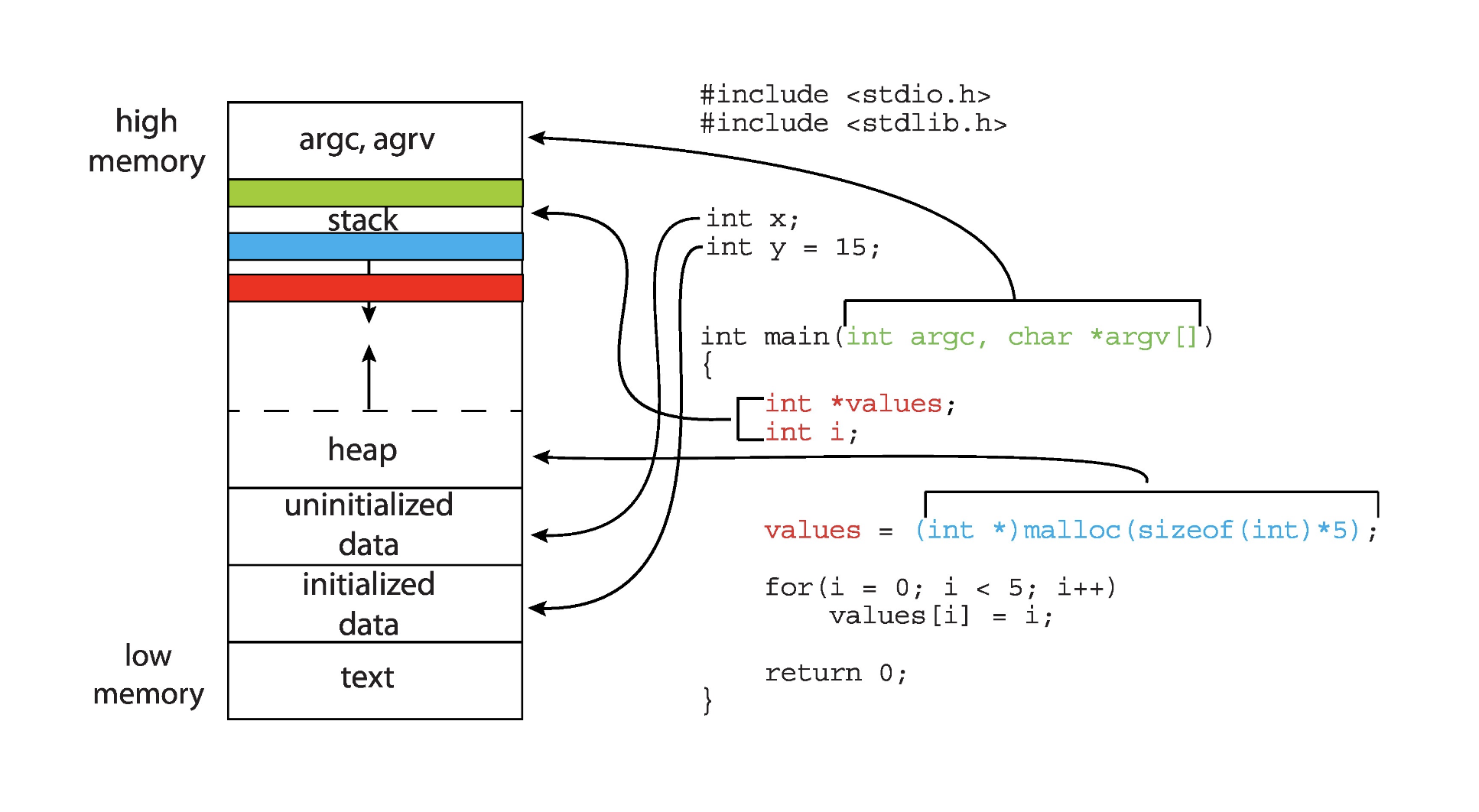
Advantages of Threads¶
Economy:¶
- Creating a thread is cheap: Much cheaper than creating a process -- Code, data and heap are already in memory
- Context-switching between threads is cheap: Much cheaper than between processes -- No cache flush
Resource Sharing:¶
- Threads naturally share memory
- With processes you have to use possibly complicated IPC (e.g., Shared Memory Segments)
- IPC is not needed
NOTE: Threads DO NOT share the following:
- Registers
- Stack
- Program Counter
- thread ID
It shares the following with other threads within the same process
- code section
- data section
- the heap (dynamically allocated memory)
- open files and signals
-
Concurrency: A multi-threaded process can do multiple things at once
-
Having concurrent activities in the same address space is very powerful -- But fraught with danger
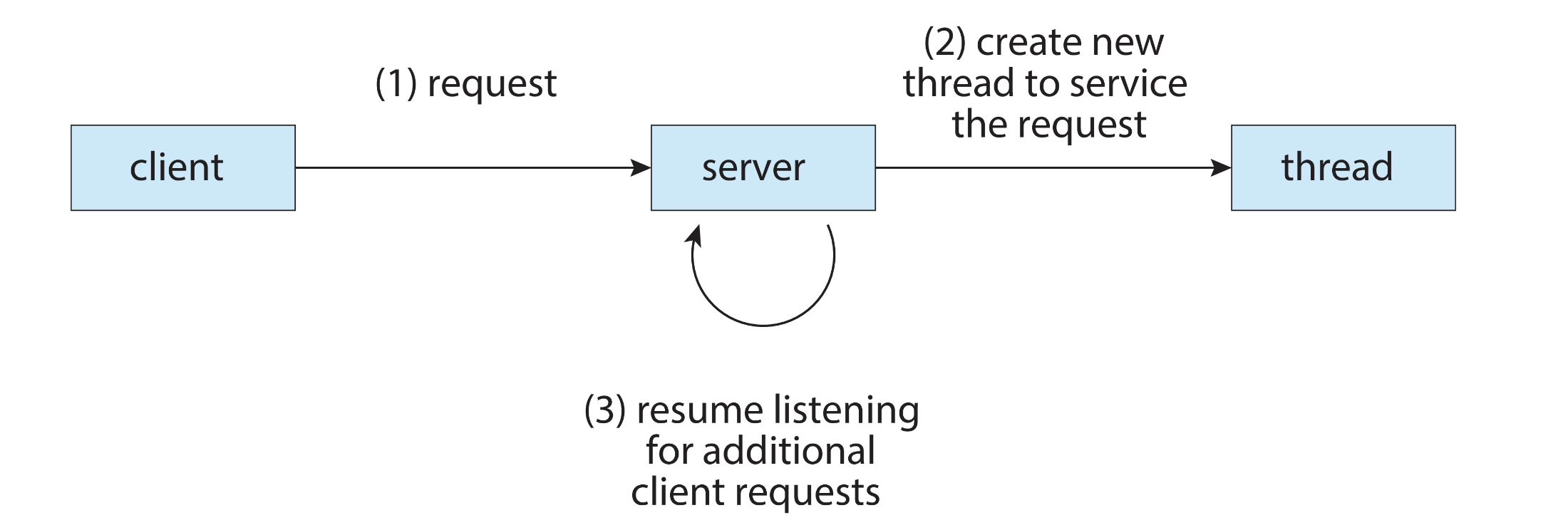
Responsiveness¶
- A program that has concurrent activities is more responsive
- While one thread blocks waiting for some event, another can do something
- e.g. Spawn a thread to answer a client request in a client-server
- This is true of processes as well, but with threads we have better sharing and economy
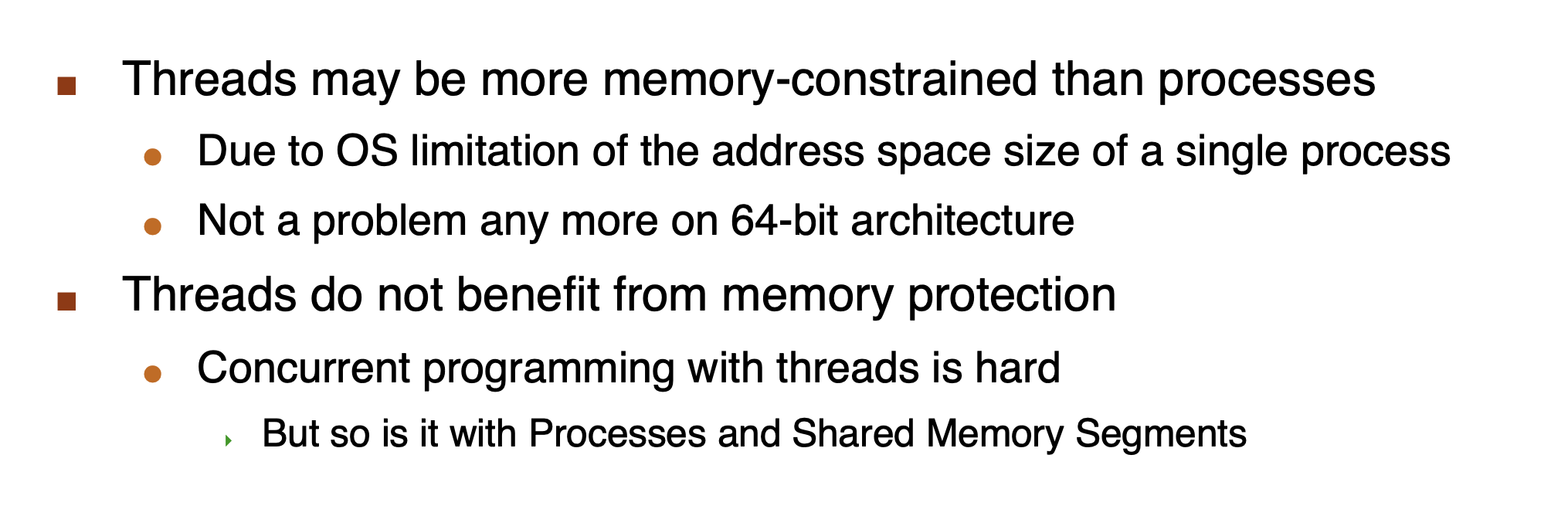
Drawbacks of Threads¶
- 隔离差

Models of Threading¶
- Linux : One-to-One
Many-to-One Model¶
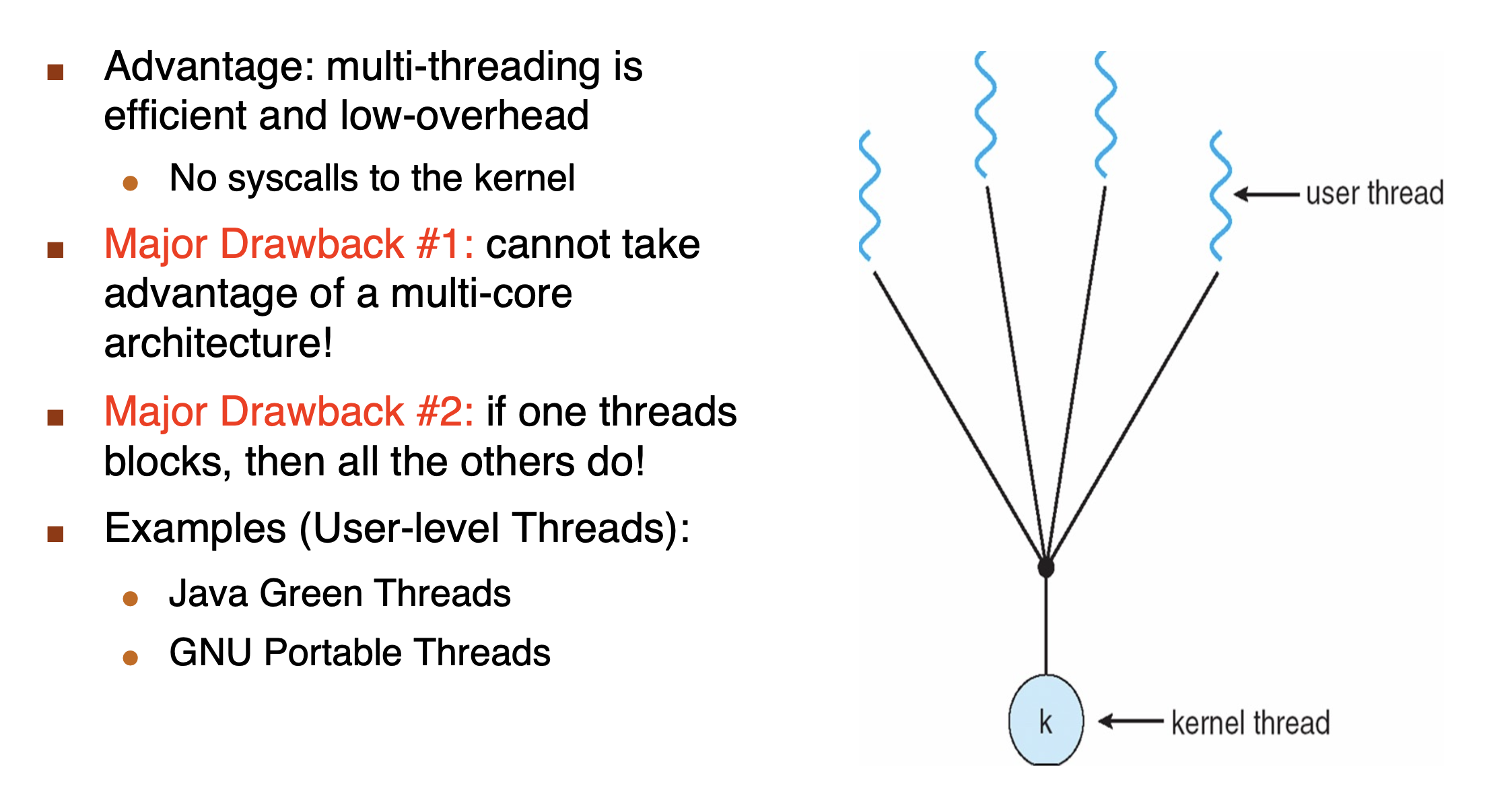
One-to-One Model¶
耗资源
- Removes both drawbacks of the Many-to-One Model
- Creating a new threads requires work by the kernel
- Not as fast as in the Many-to-One Model
- Example: Linux Windows Solaris 9 and later
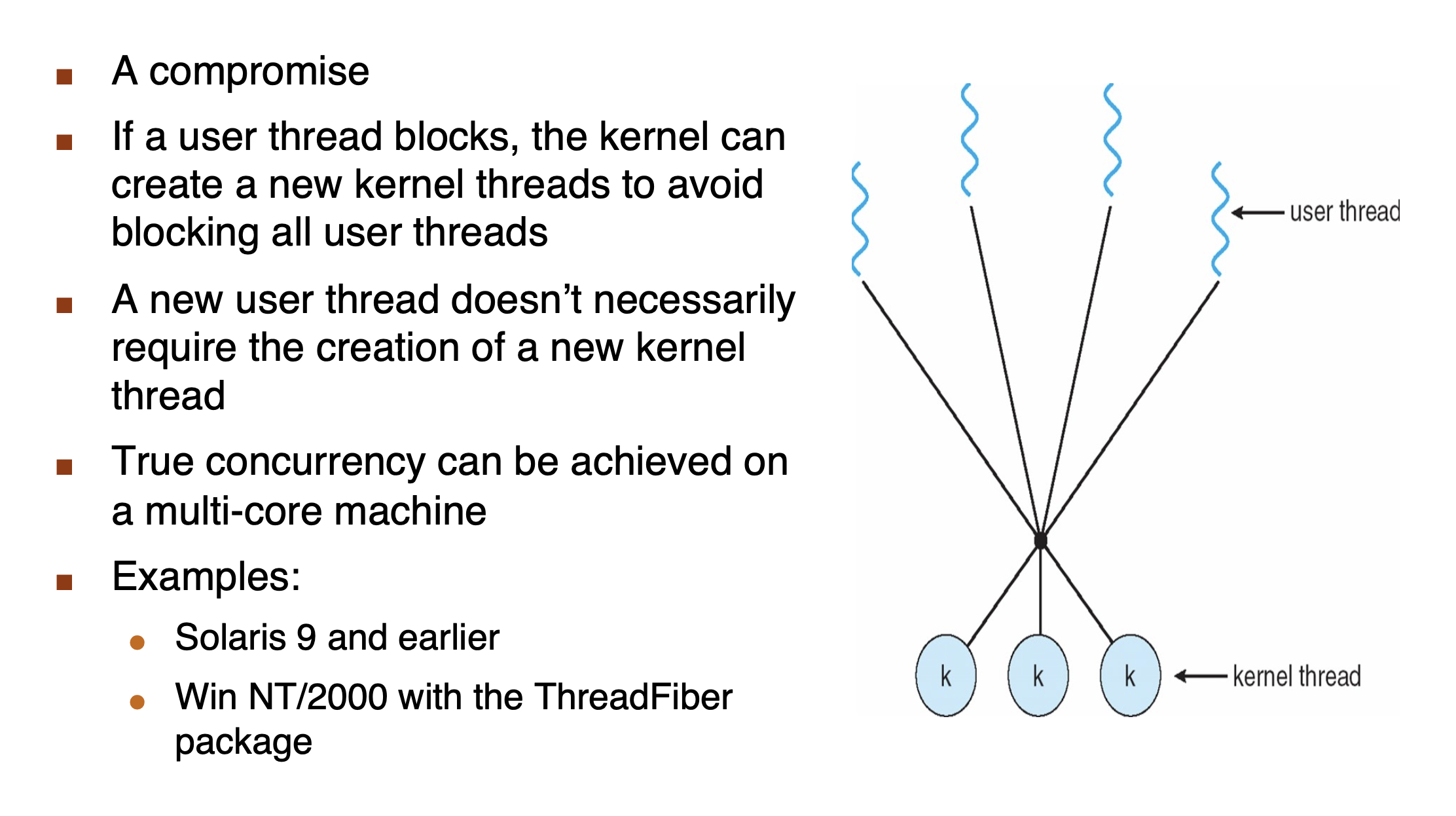
Many-to-Many Model¶
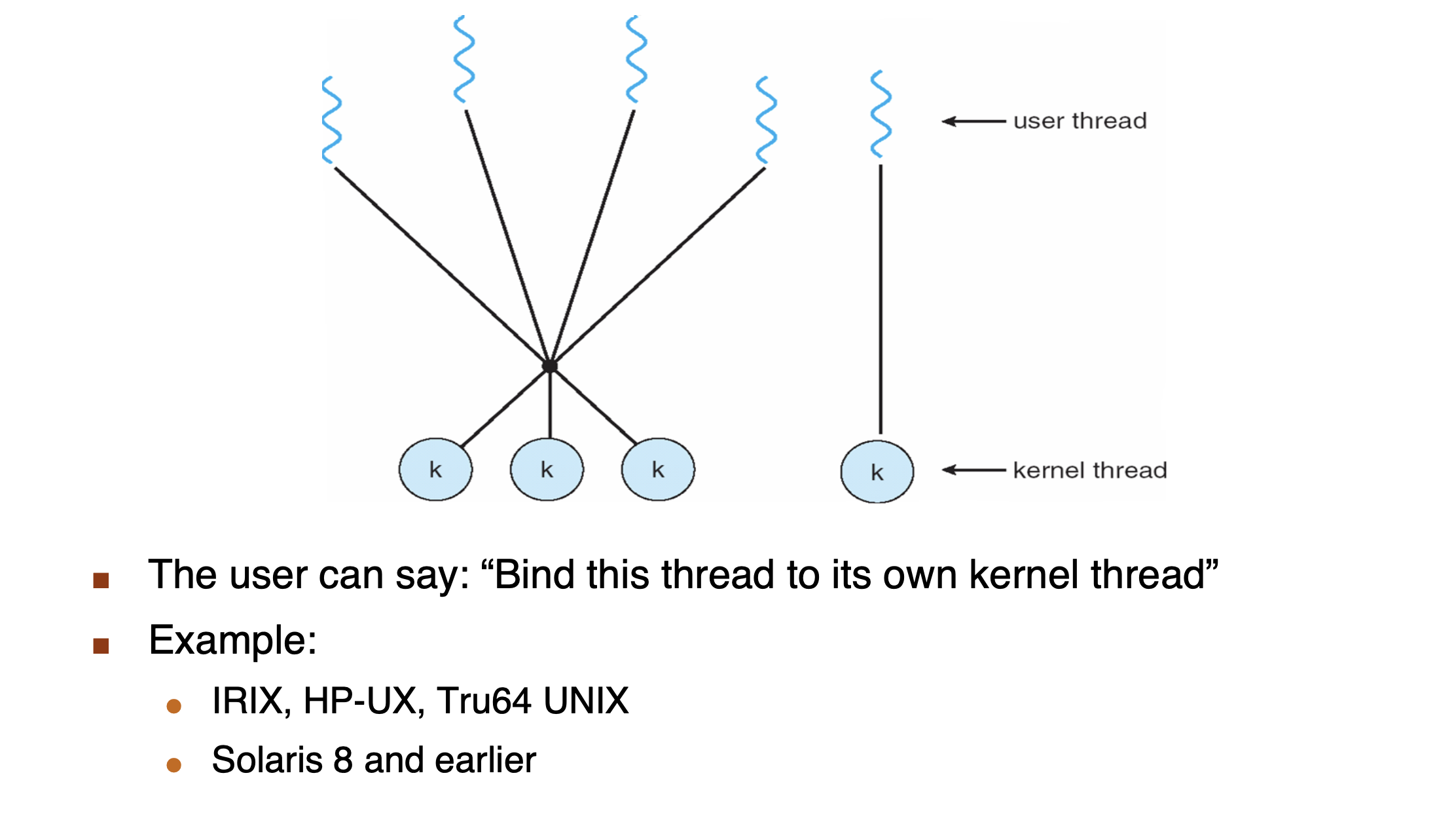
Two-Level Model¶
Threading Issues¶
-
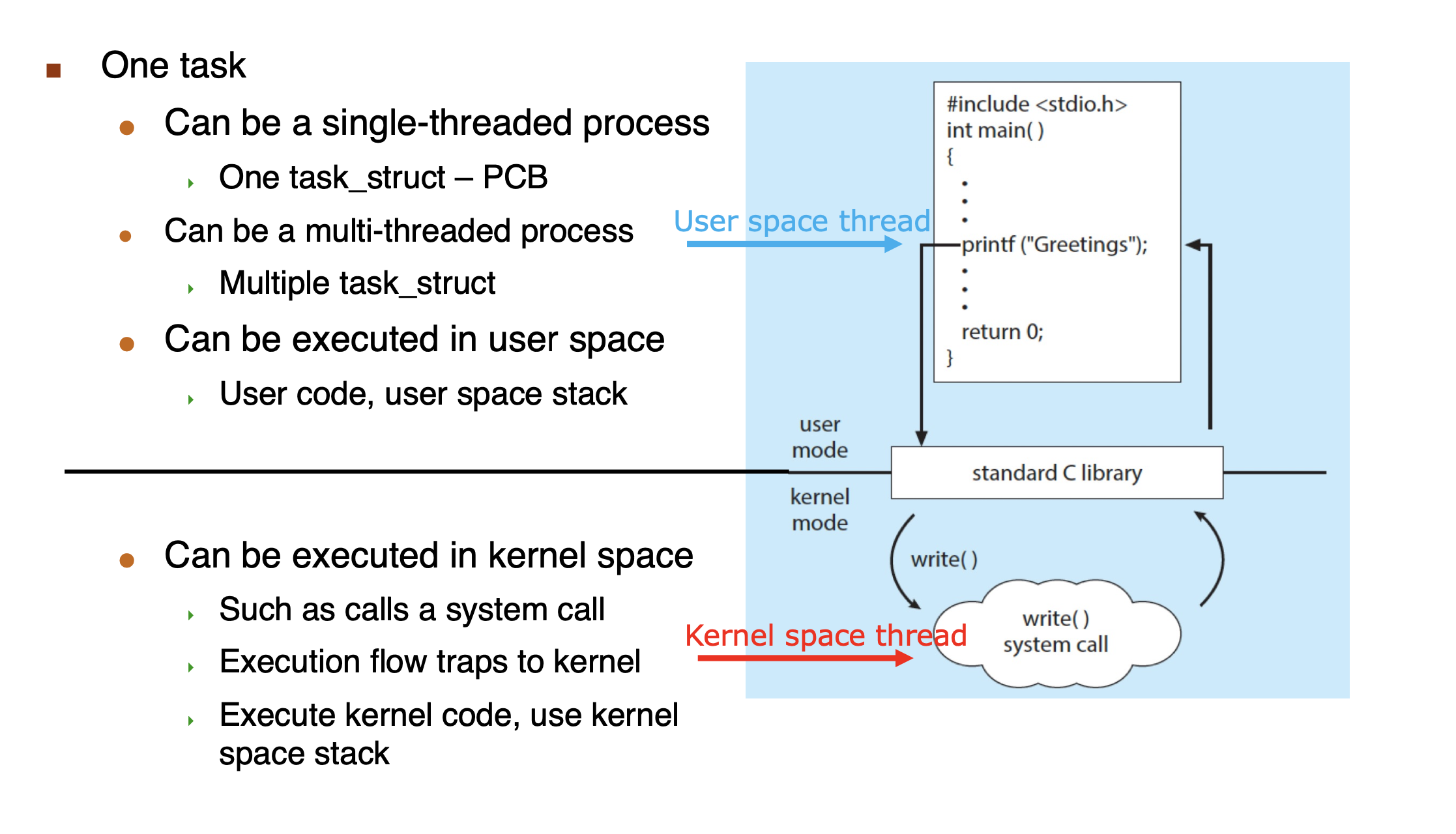
fork()andexec() -
fork()fork which thread or all threads?Linux will fork the caller thread only
exec()exec which thread or all threads?Linux : all threads are “wiped out” anyway
Safe Thread Cancelation¶
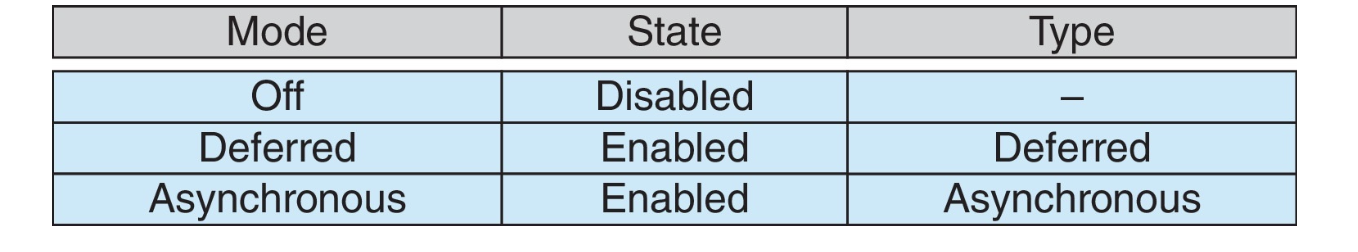
Asynchronous cancellation¶
- One thread terminates another immediately
Deferred cancellation [Default]¶
- A thread periodically checks whether it should terminate
Thread Scheduling¶
process-contention scope (PCS)
- 每个进程分到时间片一样,然后进程内部再对线程进行调度。
system-contention scope (SCS)
- 所有线程进行调度。
Linux Thread¶
- In Linux, a thread is also called a light-weight process (LWP)
- The clone() syscall is used to create a thread or a process
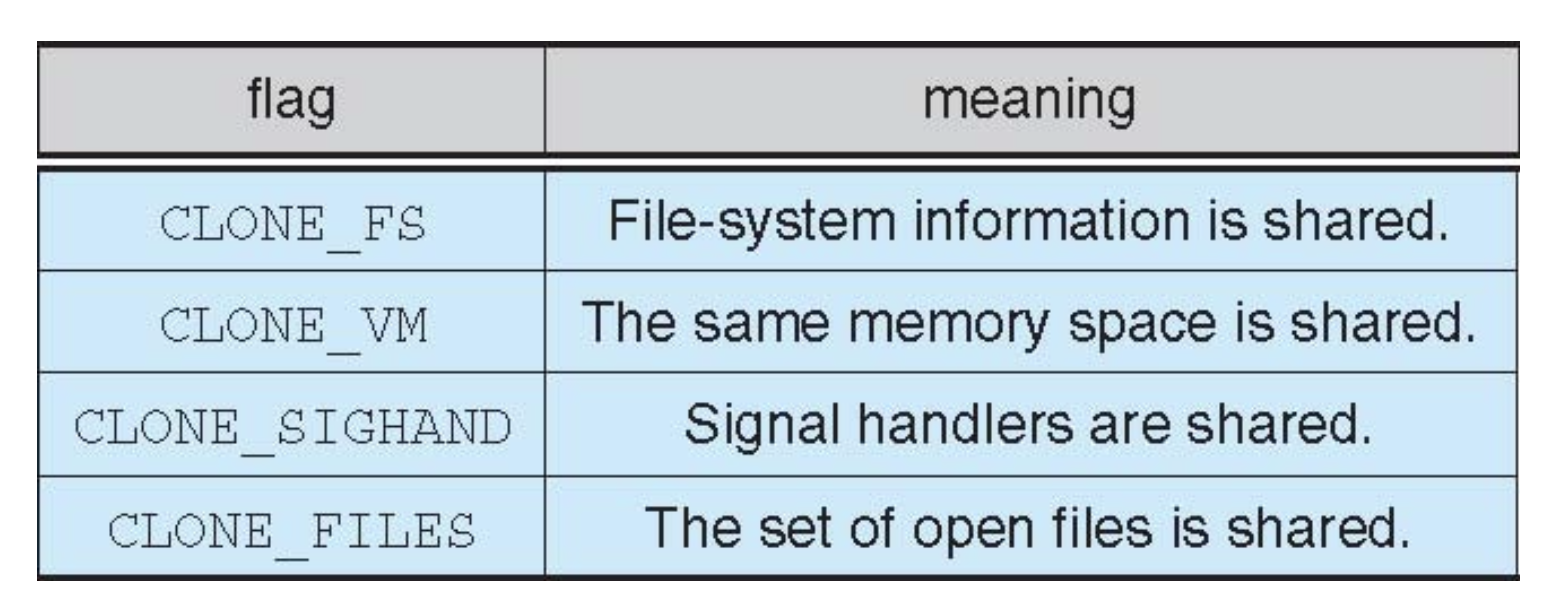
Thread Control Block -- Task Struct [TCB & PCB]¶
- When the FIRST thread is created, its Thread ID is the same as the Process ID -- Leading Thread
struct list_head thread_group- All threads in the same process are linked together
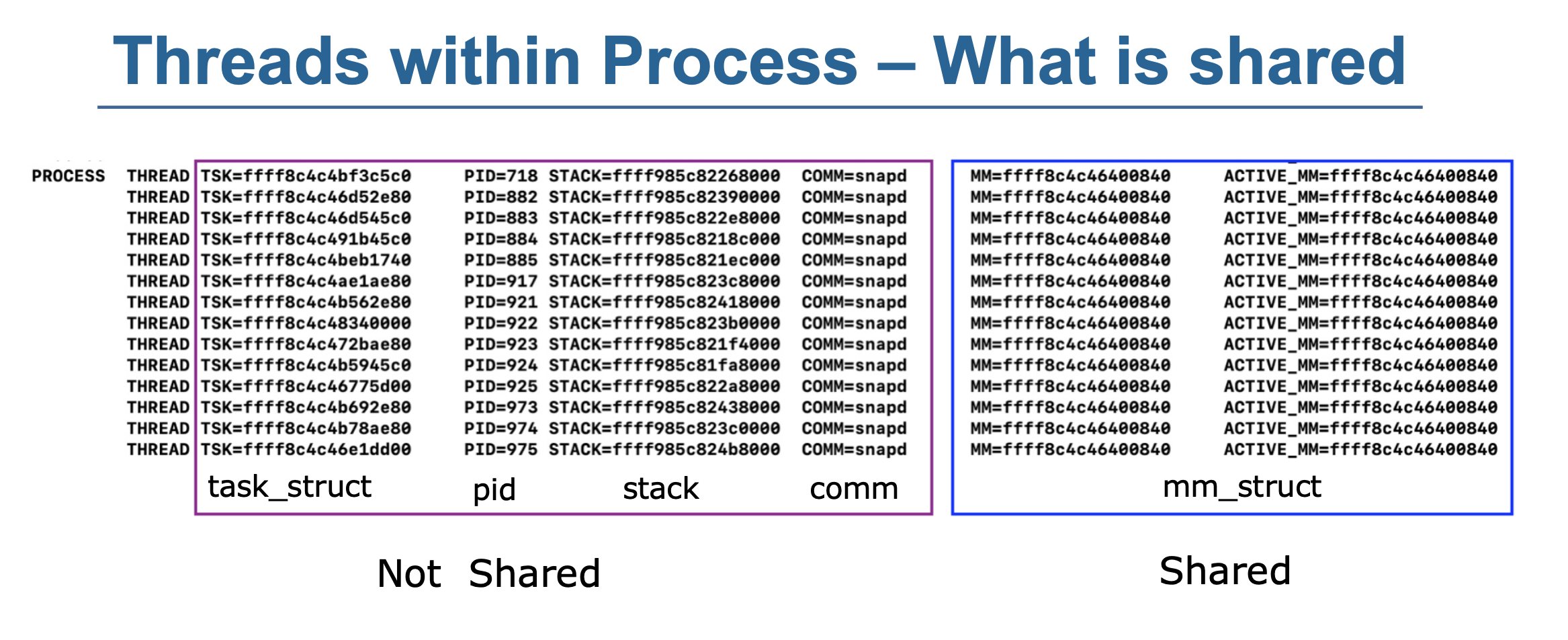
- User Space Stack 大小不固定
最后更新:
2025年1月6日 21:18:56
创建日期: 2024年12月27日 21:05:43
创建日期: 2024年12月27日 21:05:43